What Is Raw Data and How It’s Used
If you have spent some time in the corporate environment you have probably heard term raw data on numerous occasions. However, what does raw data really mean? Is it uncensored, is it yet to be digitalized, is it a bunch of numbers that don’t mean anything yet? Well, it can mean a lot of things, and here we will explain raw data in-depth and also provide explanations on how it is different from other types of data.

Aug 21 2020●2 min read
Raw data definition and explanation
When we say raw data, we typically refer to data that is readily available but cannot be easily used speaking. Raw data is compiled from multiple sources, and different sources can often mean that information is displayed in various formats.
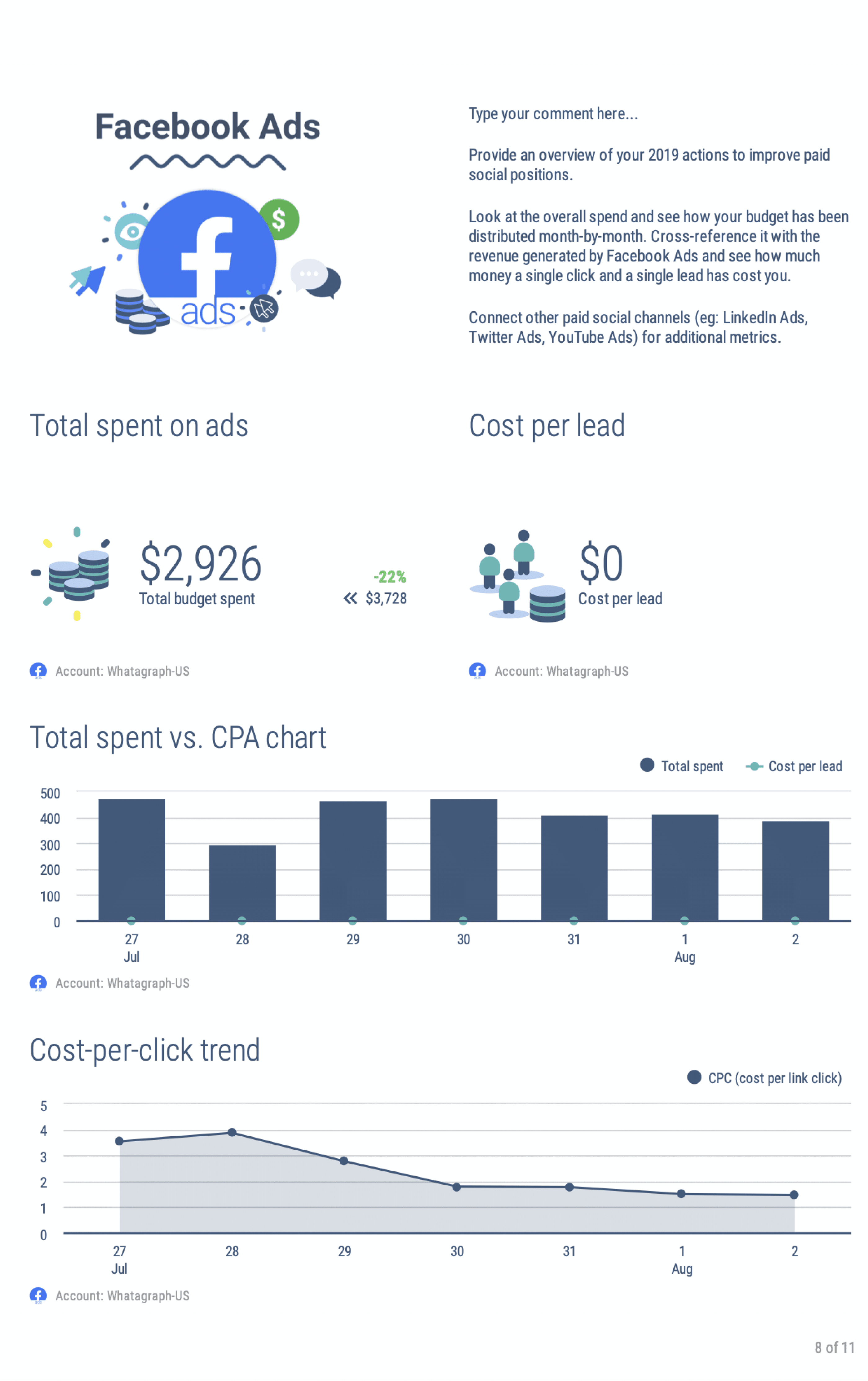
For example, if you want relevant metrics for your online shop, you might get several website visits per month. That number is raw data as it does not offer anything related, except the number of visitors your site had over the past 30 days. For you to extract meaningful insight from that number, you will have to process the data over and over again, using filters, algorithms, or other means that help you get more concrete details.
If you have an e-commerce site, you probably want to know how many people bought the product or how many abandoned their carts. Also, you want to see the site’s bounce rate, whether visitors find websites via organic search or referral. And where your shoppers are located, etc. There are so many useful metrics that can be extracted from raw data, which is why it’s valuable but not useful on its own at the same time.
Difference between data and raw data
Now that we covered what is raw data, it’s easy to assume what the term processed data, also known as data, would entail, right? Well, not exactly. Processed data can always be processed further, or you can extract even more precise information, so even just saying processed data can be too general.
So to make a better clear distinction, let’s say that data is the product of organizing raw data and turning it into a unified product that’s easier to manipulate or navigate. To do this, we use SQL or structured query language to achieve the desired format and effectively communicate with the database. However, the main difference is that you cannot do useful data analysis on raw data, whereas you can do data analysis on data or processed data.
Many tools allow you to this intuitively like Whatagraph. Even if you are not a developer or know how to code, you can still perform data analysis, have unified file formats, and make relevant data input in a formal report using primary database or data from different sources.
 Why is raw data important?
Why is raw data important?
Although raw data can take a considerable chunk of space on storage devices, you should not remove it or delete it once it has been processed. Processing data implies that you are going to filter out information and remove you deem redundant, or put them in a different context. Having access to raw data allows you to trace back those decisions and ascertain whether original processing was done correctly. In other words, data processing and data analysis is also trial and error experience, so having access to a source data is a must.

WRITTEN BY
Indrė Jankutė-CarmaciuIndrė is a copywriter at Whatagraph with extensive experience in search engine optimization and public relations. She holds a degree in International Relations, while her professional background includes different marketing and advertising niches. She manages to merge marketing strategy and public speaking while educating readers on how to automate their businesses.