SEO Analytics: A Comprehensive Step-by-Step Guide
This guide will introduce you to SEO analytics and help you become more familiar with optimization efforts. You'll discover that SEO analytics is more than simply data; it's data and ecosystem. Consider data to be words, and the ecosystem a combining material that helps to make sense of those words. Learn how to interpret SEO statistics and how to make your marketing efforts more effective.

Feb 11 2020●15 min read

What is SEO Analytics?
SEO analytics is defined as a method of collecting and analyzing your data to gain a better understanding of your website's organic performance. An effective SEO analysis helps identifying key areas to focus on when optimizing your site for search engines. To master SEO analytics and report on SEO data, use tools like Google Analytics or Google Search Console.
5 Types of SEO Analysis
SEO content audit
A standard definition of an SEO content audit - the process of evaluating current content on your website in order to determine how you can get more high-quality traffic to each page. An SEO content audit also helps to identify areas for improvement to increase conversions.
Auditing content will provide you with information on which blogs/e-shops and pages:
- Are seeing a drop in search traffic. This could be due to seasonality, technical issues or algorithm changes;
- Are affecting your overall website performance in a negative way;
- Are providing value to SERPs and website visitors alike.
Site audit
A site audit is one of the most comprehensive reports evaluating the overall performance of a website. It combines all the pages' to provide an overall SEO health score.
Improve your site's performance by implementing an SEO audit into your SEO strategy and benefit from:
- Identifying any issues that may exist on-site or off-site;
- Enhanced keyword distribution;
- Detailed competitor analysis to discover successful strategies.
Off-page SEO
Off-page SEO, also known as off-site SEO, refers to actions taken outside of your website to impact the rankings within SERPs.
This is where you'd analyze:
- Distribution of anchor text;
- Quality of link sources;
- Number of backlinks to certain pages;
- Referral traffic from backlinks.
To have a strong backlink profile, there are even more things that an SEO specialist should consider:
- Incorporating a large number of organic, relevant, and high-authority backlinks;
- Natural anchor text selection;
- Keep the number of low-quality links as low as possible. Disavow spam links using Google Search Console.
In other words, backlink profile analysis shows the aggregate quality of backlinks your website has managed to acquire over time. Tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush, Surfer SEO or its alternatives have their own proprietary way of measuring the overall backlink quality of pages using Domain Rating and Domain Authority.
Interestingly, according to fresh research from the link-building provider Editorial.Link, which surveyed over 500 SEO professionals and marketers, found that the most effective off-page techniques in 2025 are SaaS link building, Digital PR, Guest Posting, and creating Linkable Assets.
On-page SEO
On-page SEO, also known as on-site SEO, is the application of SEO best practices to the content you create in the hopes of improving its ranking in search results. On-page SEO analyzes:
- Headings;
- CTR of queries;
- Title tags;
- Content;
- Internal link structure.
But the list doesn’t stop here. As described in this on-page optimization checklist from GOTCHSEO, other factors can influence your ranking in Google, so make sure you identify the ones relevant to your site.
On-page SEO tools data analysis benefits specialists by providing data that identifies areas for improvement. This data can then be used to try:
- Optimize content with newly acquired data;
- To expand reach by capturing more relevant keywords.
It can also provide data on the audience of your website, particularly location data, that can help with decision-making on how to expand the site. If your analytics determine a potential audience in a region that speaks a certain language, it might be worth investing in SEO translation to create well-optimized multilingual content.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is a method in which the goal is to ensure that the site meets the technical benchmarks of current search engine standards. Furthermore, technical SEO analysis aids in the improvement of organic rankings. Here are some of those benchmarks:
- Page loading time. You hurt your ranking by not optimizing website speed. Google prefers web pages that load quickly, as this characteristic indicates a better user experience;
- Dead links. The more non-existent landing pages and broken links there are, the worse the user experience becomes. SEMRush, a SaaS platform for SEO optimization, includes a 'Broken Link Checker' feature that can help you find broken links on your website;
- Duplicate content. The presence of duplicate content confuses search engines. They are unsure which content is better and should be ranked higher. This minor error has the potential to harm both content pieces and lower their rankings;
- Website security. Technical SEO audits also ensure that your website is secure. Privacy is a minimum necessity for search engine users, and you must focus on ensuring that it is met. Implementing HTTPS would be one solution. They guarantee that no one can hijack data transmitted between the browser and the site. A secure website is ensured with a targeted VPS hosting provider for a certain location, such as VPS Europe.
This is critical because, once again, search engines like Google recognize the importance of security and, as a result, rank websites with HTTPS higher.
How Do You Analyze SEO Data?
To conduct a perfect and thorough SEO data analysis, follow these 7 crucial measures.
Check your page speed
"Two seconds is the threshold for eCommerce website acceptability. At Google, we aim for under a half-second". According to research, even a one-second improvement can increase online revenue by 7%. Not only that but the negative side of slow loading time could be increased bounce rate and decreased satisfaction with your UX and UI.
As you want your visitors to enjoy 'their stay' on your website, you should check your page speed with, for example, Google PageSpeed Insights. After doing that, try to fix the areas that slow your website down. Usually, to improve the website loading speed, the advice is to:
- Enable caching.
This means that a visitor's browser downloads your website's resources (e.g. JavaScript files or images). Doing that is critical to speeding up return visits;
- Minimize HTTP requests.
If you get more than 50 HTTP requests, you need to focus on reducing this number. Deleting unnecessary images and reducing image size would be the very first things to do.
- Choose, if needed change, the hosting option.
Consider web hosting services that you are currently using. Maybe there is a business offering a better-optimized web with faster load speed.
- Compress files.
Compressing files reduces data transmission time. Use youcompress and compress images, videos, and any doc.
Interesting insight: 3rd party code like GTM and Hotjar could potentially slow down the performance of your website. This is due to the extensive list of tags that marketers use on their websites to track and assess user behavior. Make sure you use tags only on the most necessary pages, pause tags that aren’t in use, and remove the ones that delay the scroll.
Check your visibility on Google
SEO visibility on Google is defined as a measure of how visible a site is in organic search results when queries are entered into search engines on desktop computers.
This visibility gives an insight into:
- How well you are targeting specific keywords;
- How easy it is for Google to crawl your pages;
- How compelling are your titles;
- How well you optimized your website.
Here is a website where you can check your visibility. It will inform you of your website's visibility on mobile and desktop devices. Alternatively, you can get valuable and actionable search visibility insights for the specific region and time period by performing a Google Ranking Check with SE Ranking.
Audit your images
Image optimization influences the way search engines calculate your site rank. To make sure your SEO efforts are successful, back them up by:
- Go through image descriptions and update or include alt texts and image file names;
- Compress image files;
- Optimize your images and files so they are mobile-friendly. In 2018, over 50% of worldwide web traffic was generated through mobile phones.
Nick, the CEO of DataforSEO, discusses his thoughts on large media files:
"One thing I noticed on a lot of websites are huge media files that slow it down significantly. Businesses want to show high-resolution images which is perfectly fine. However, if those aren’t optimized for SEO, they can create huge issues. Some websites even crash because of the inappropriate size. Videos fall in this category as well. They make it almost impossible to scroll on the website if they take too long to load".
Check your URLs
To analyze your URL, Google has provided a free inspection tool that includes information such as:
- AMP (accelerated mobile pages) errors;
- Structured data errors;
- Indexing issues.
Analyze Your Website Content
Auditing website content provides a chance to rank higher than before. You want to stay relevant and up-to-date with your content if one of the goals is to be more visible and increase CTR.
Here are 4 frequently used steps in a website content analysis:
- Page title. Usually, it is recommended to keep the title at 50-60 characters, have the word HOW, WHAT, or WHY, and have the main keyword you are trying to rank for;
- Target keyword.
Mike Lowe, Founder & CEO of Growthsaloon.com shared his insights about keywords:
" Many SEOs go back and forth on this one. But I've found it's better to try to rank high for 1 keyword rather than try to rank decently for multiple keywords. If you match your H1 and your Page Title, Google can better understand what your page is about. My motto is that it's better to rank Top 10, Top 3, or #1 Overall for 1 keyword - instead of ranking on Page 2 and beyond for multiple keywords".
3. Meta description. Make sure your description is within the character limit and has a keyword. Here is a SERP Snippet Optimization Tool that allows you to write meta descriptions and titles that fit the word limit;
4. Secondary keywords. These are usually similar to the primary keywords, yet they play a supporting role. Add secondary keywords by addressing the nuances and subtopics about the related primary keywords that the user is interested in. This will demonstrate to Google that you're a professional who understands things and user intent.
Evaluate Backlinks
Look at the backlinks your content pieces have. See if any of them are spammy and compare the backlink numbers with your competitors. Here is a tool to do that serpstat. You ideally want to have as many high authority backlinks as possible. That means links from high-quality websites that have good SEO performance, and are relevant to your niche.
As an expert SEO puts it:
I like to look at a couple of things when assessing a potential backlink. First, the usual—organic traffic and Domain Rating. I tend to aim at domains with rising traffic of at least 5,000 and a DR of at least 40. Next, I take a quick look at the cache date on the desired article. It tells me whether that particular piece has been recently crawled, which is a signal that Google likes that URL. If you can easily buy a link on said domain, it’s a no-go for me. Websites that don’t have any specific topical range are also weak in my mind. Finally, using the site: command on Google, I check whether the site has any risky content such as casinos or essay writing.
Milosz Krasiński, International SEO Consultant, Speaker, and Blogger.
Check Your Internal Links
Internal links refer to the links that go from one page to another within the same domain. In other words, it's when you put one blog's link on another blog. To add, internal links build a site structure to help Google better assess what the content is about and how your whole website relates to various topics. Investigating internal links will provide a smoother user experience for visitors.
Consider a user who visits your blog and clicks on one of the links only to discover that the link is broken or that the material is no longer available. You should go over your links and eliminate any that don't serve a function if you want to reduce these flaws and give your site a more professional appearance and improve user experience.
SEO Metrics
SEO metrics are data sets or signs that should be tracked and monitored to maintain a high-performing and optimized website. This is one of the most extensive and detailed SEO metrics lists you'll find online:
- Leads: SEO leads are potential clients that find your website, services, or products through search engine results;
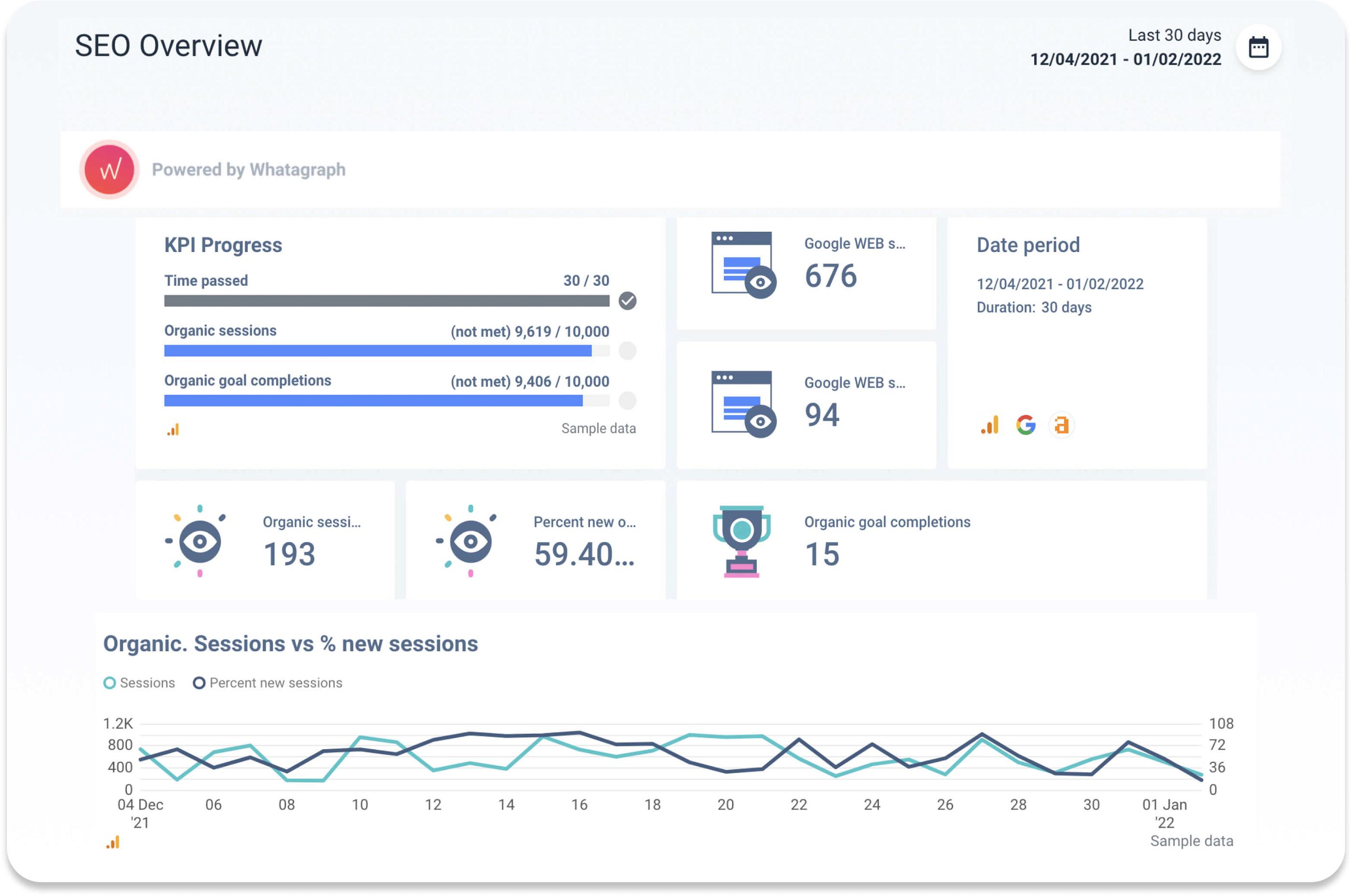
- Organic Traffic: Visitors that land on your landing page or website from unpaid sources are generating organic traffic. Two important indicators to include in SEO analytics are organic traffic source and total organic traffic.
If you connect your Google Analytics 4 account with Whatagraph, you'll find your organic search traffic metrics in one comprehensive report or dashboard;
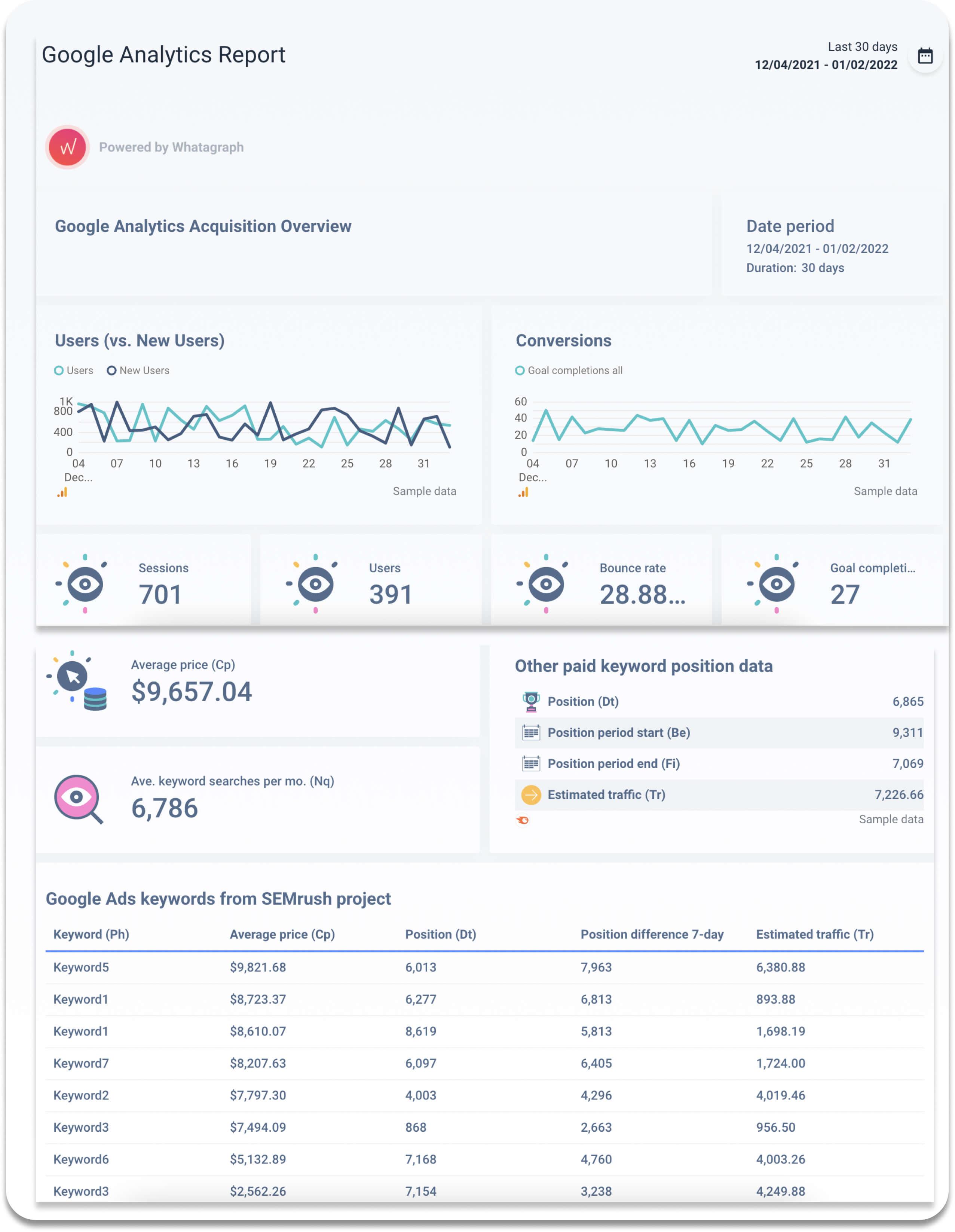
- Referral Traffic: Refers to the traffic, when visitors come from outside sources or other websites;
- Keyword Rankings: The position of your page on the search results page for a specific search query is referred to as keyword rankings in SEO. Tracking this metric will provide actionable insights into how your keyword and website with that keyword is performing in Google;
- Bounce Rate: In web traffic analysis and in SEO, the bounce rate is a metric represented in percentages, showing visitors who visit one page before leaving;
- Pages Per Session: Curious about how many pages a person views in a single session? Pages per session will give you this percentage. The higher the percentage, the calmer you can be as it indicates that your content is interesting and your UX is smooth;
- Page Views: This metric indicates the total number of pages viewed. Google Analytics counts repeated views of a single page by the same viewer;
- Average Time On a Page: This measure calculates the average amount of time spent on a single page by all website visitors. According to several marketers, their average time on page is between 2-3 minutes. Others use "read time", which is calculated by averaging the number of words in an article and the words per minute speed of a typical reader;
- Top Pages By Page Views: If you want to find your top landing pages or blog posts, track top pages by page views. Google Analytics and Whatagraph is the go-to combination to easily learn about this metric. Connect your Google Analytics account to Whatagraph, and you'll automatically be presented with a comprehensive, visually appealing, and easy-to-understand report (or dashboard);
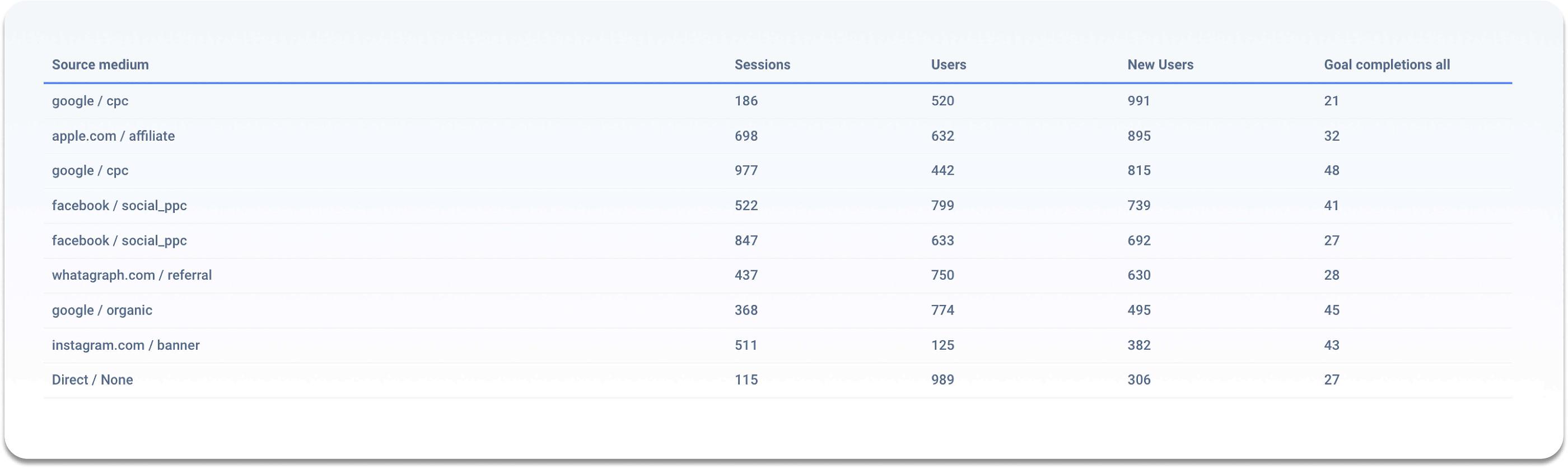
- Conversions: Marketing teams define SEO conversions as a fulfilled desired action by website visitors. Those actions could include downloading a guide, filling in the form, or signing up to an email list. The average decent SEO conversion rate for B2B SaaS companies is considered to be 1.1%;
- Average Page Load Time: You should be tracking this number just to make sure that your mobile and desktop average page load times are not too long. As already mentioned, the ideal load time should be no more than 2 seconds;
- Organic Clickthrough Rate (CTR): CTR tracks the number of people who click on a search engine result. Organic click-through rate is mostly determined by ranking position, but it is also influenced by a result's title tag, description, and URL. The primary purpose of CTR tracking is to gauge engagement and gain a better understanding of your customers. This measure reveals which material your audience finds fascinating, which pages they find uninteresting, and even which pain points they have.
- On-page Optimization Scores: On-site SEO score tells you how well the user-facing and technical aspects of your site contribute to search engine optimization, organic traffic, and higher rankings. You can use seositecheckup.com to find your general SEO health score and improve it by following their advice;
- Impressions: Google defines impressions as the number of times a URL from your site was displayed in a user's search results, excluding paid Google Ads search impressions;
- Traffic cost: The traffic cost is an estimate of how much bidding on organic keywords through Google Ads will cost.
Setting Up Tools
Now let's talk about the tools you could use to perfect your SEO analyses.
Whatagraph
Whatagraph is a tool that allows marketers to track campaign results across several platforms. Build detailed SEO reports and let data insights lead the way. Using our automated SEO reporting tool, you can assess the effectiveness of your search engine optimization efforts. Whatagraph connects with Google Analytics, Google Search Console, SEMrush, and Ahrefs, among other SEO tools. Our SEO reporting software allows you to track any of the already mentioned metrics and visually present them so that you can immediately learn about your website performance.
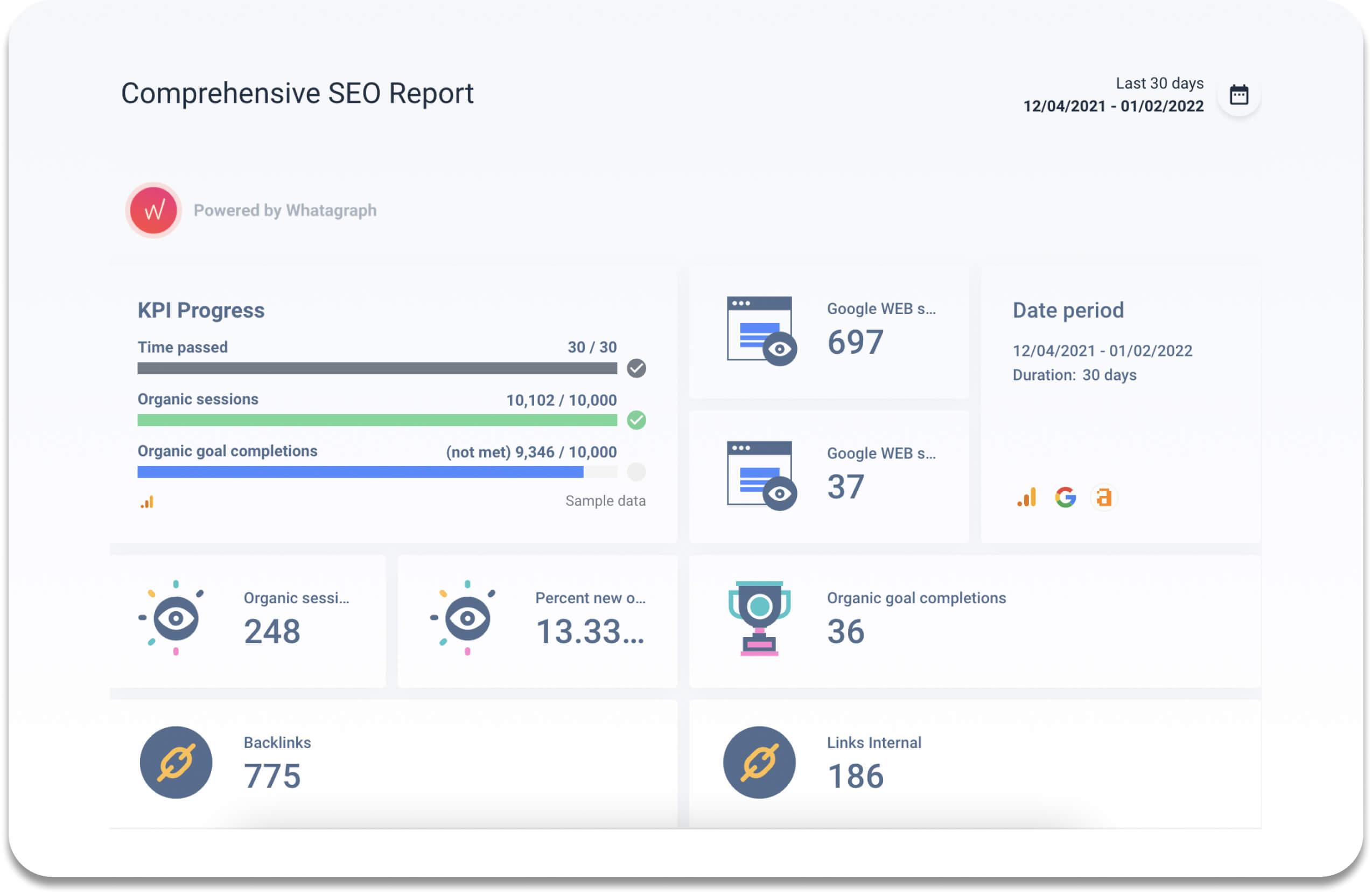
Whatagraph's features assist marketers to spot patterns in how visitors interact with their website. Those features include:
- Data analysis, monitoring, reporting, collection, and visualization;
- Data visualization with scorecards and motion charts that display changes in data over time;
- Cross-channel reporting to help you analyze data and compare different channel performance in one place;
- Funnel analysis;
- Data collection APIs;
- Custom reports for advertising, acquisition, audience behavior, and conversion;
- Email-based sharing;
- Interactive dashboards and reports.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a web analytics platform that offers basic analytical tools and statistics for search engine optimization (SEO). They use page tags to collect user data from each viewer.
A JavaScript page tag is inserted into the Google Analytics tracking code of each page. This tag collects data from each visitor's web browser and sends it to one of Google's data collection servers. Google Analytics then generates customizable reports to track and visualize data such as:
- The number of users;
- Bounce rates;
- Average session durations;
- Sessions by channel;
- Pageviews;
- Conversion rates.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console (formerly known as Google Webmaster Tools) is a free service that allows you to manage and troubleshoot the appearance of your website in search results. It can be used to detect and resolve technical faults, submit sitemaps, and view backlinks.
Bing Webmaster Tools
Bing's Webmaster Tools is a useful tool that allows website owners to keep track of their site's status in Bing's search results. It provides search data like:
- Site traffic;
- Rankings;
- Indexing.
Ahrefs
Ahrefs is an SEO software suite that contains tools for link building, keyword research, competitor analysis, rank tracking, and site audits. With Ahrefs acc:
- Identify Keywords;
- Audit your site;
- Check Website's Content;
- Track your ranking;
- Check Backlinks of Competitors;
- Identify Broken Links.
Ahrefs features the largest backlink index of any tool on the market. You may use this tool to monitor your competitors' SEO methods, backlinks, keywords, and other factors. If you're on a budget though, there are some alternatives to Ahrefs which perform a similar function at a lower price.
SEO Analytics Reports & Dashboards
Whatagraph provides a variety of template and widget options to assist you in quickly creating a custom SEO dashboard or report. They’ll be as detailed or as brief as you want them to be; either way, they’ll be equally visually appealing and easy-to-understand.
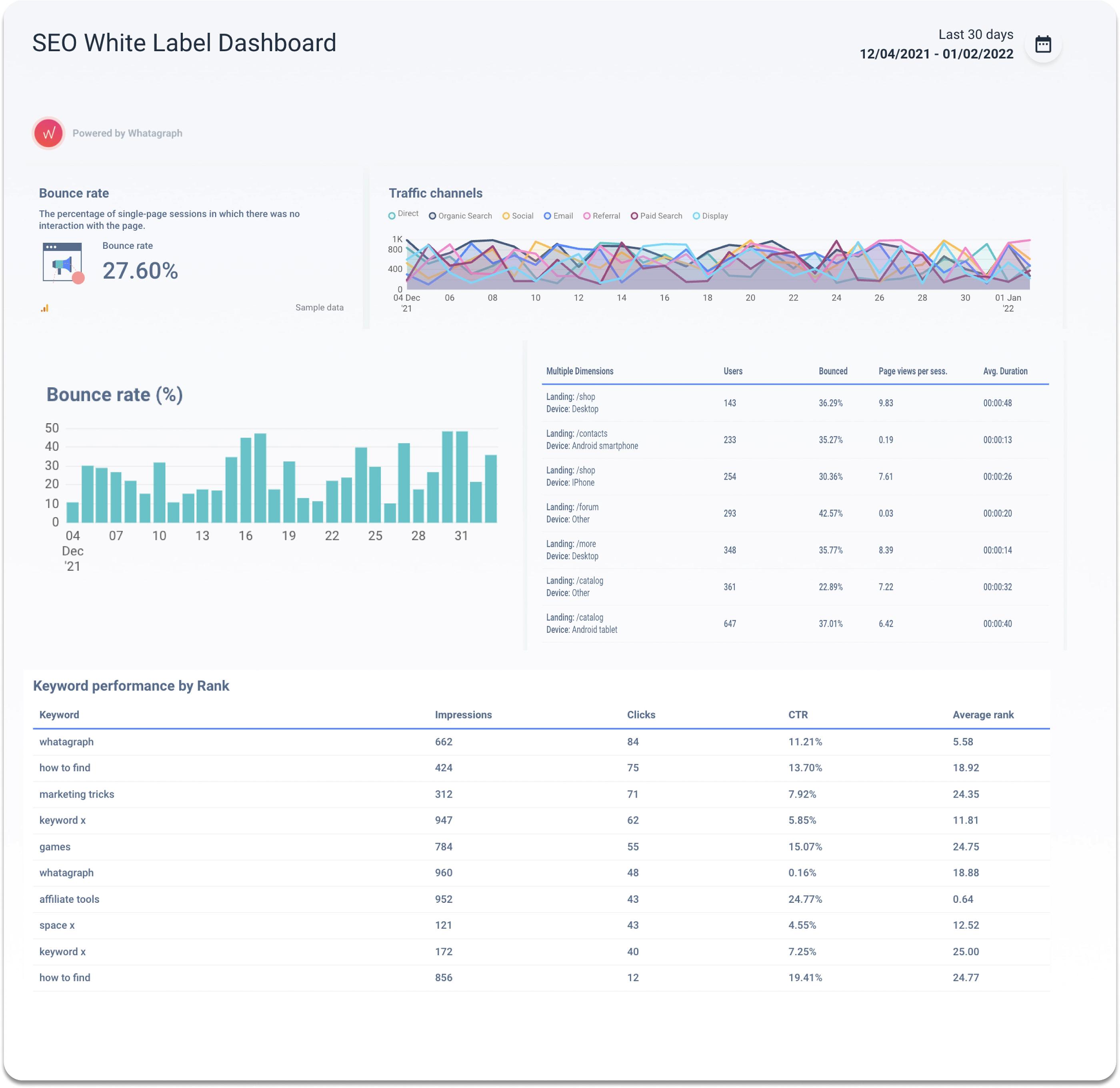
One of the most popular SEO dashboards is the SEO White Label Dashboard. Specialists would create this dashboard to view: keyword rankings, top-performing pages, CTR, and other metrics to demonstrate the success of your SEO efforts.
SEO White Label Dashboard assesses:
- Top landing pages;
- Traffic sources;
- Bounce rate;
- CTR;
- Organic keywords.
If there was a need to compare website SEO results to the objectives, a Google Analytics SEO report would come in handy. Whatagraph can be connected to a Google Analytics account to allow for simple tracking of KPI progress. One of Whatagraph's features, 'goal widgets', lets specialists easily track the success of their SEO objectives. They can even set a timeframe for achieving those goals.
Sometimes SEO specialists need access to a bit more information. Whether it is to find data patterns or understand current tendencies. A comprehensive SEO reporting dashboard connects to the most popular platforms, such as Google Search Console, Google Analytics; or SEMrush, and provides access to all of the key SEO insights and metrics in one place.
Lastly, we have to mention Keyword Ranking Reports. You wouldn’t find a single SEO specialist that wouldn’t need one! Start tracking and filtering targeted keyword rankings to identify top keywords and make informed content creation decisions.
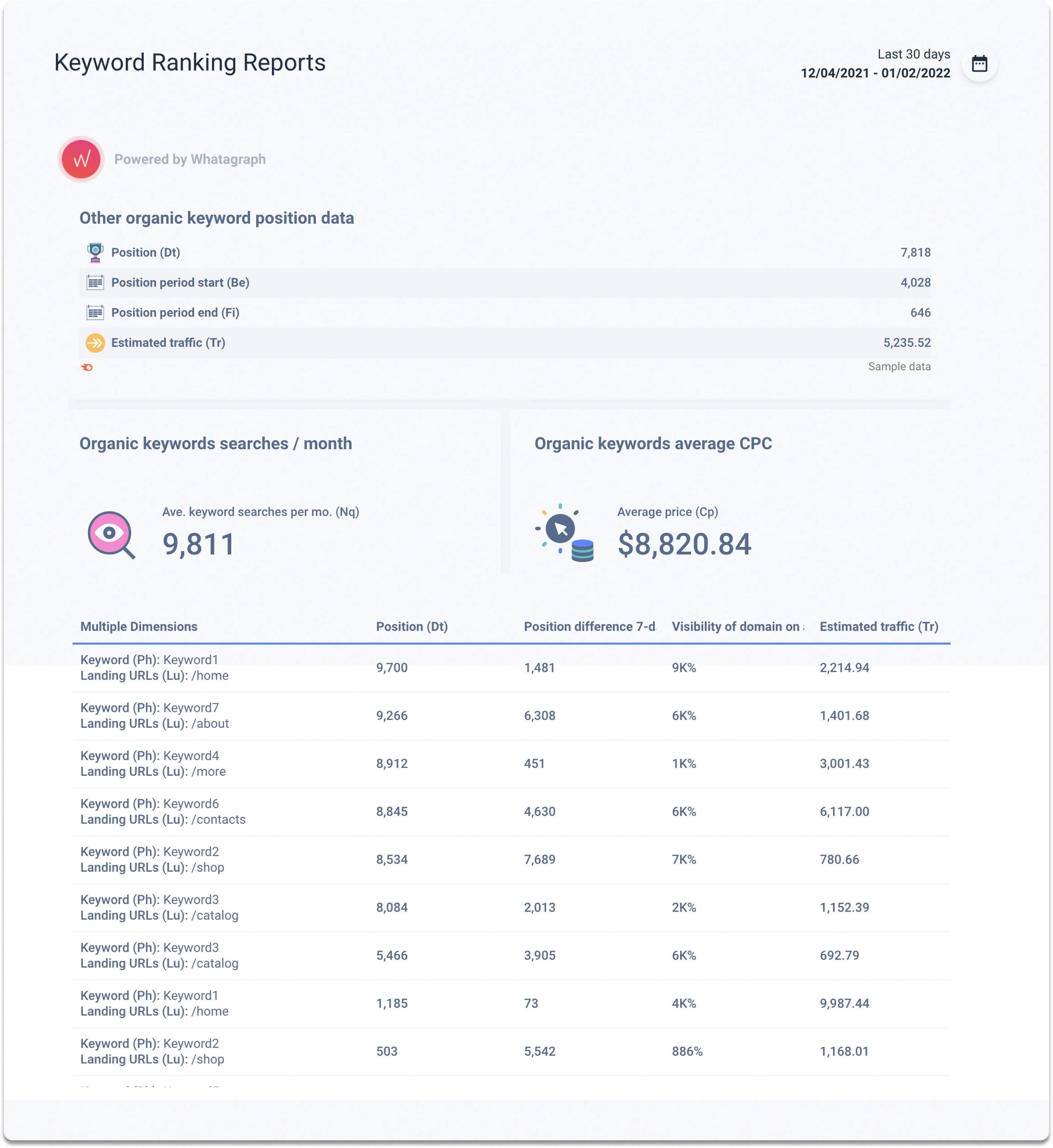
Whatagraph’s Keyword Ranking Reports automatically pull up-to-date insights and can even schedule them to be sent out at your convenience - daily, weekly, monthly, or even quarterly. Create and distribute comprehensive performance reports in a fraction of the time.
Bottom line
One of the most advantageous aspects of running an SEO campaign is that you will generate a large amount of data to work with in the future. This data will enable you to make data-driven decisions and develop better strategies.
To take advantage of this data and create successful SEO roadmaps you need an analytics tool. Sign up for a free 7-day trial of Whatagraph and start generating SEO reports that are most valuable to you.

WRITTEN BY
Dominyka VaičiūnaitėDominyka is a copywriter at Whatagraph with a background in product marketing and customer success. Her degree in Mass Communications/Media Studies helps her to use simple words to explain complex ideas. In addition to adding value to our landing pages, you can find her name behind numerous product releases, in-app notifications, and guides in our help center.